Ward Level Health Insurance in Nepal: A Comprehensive Guide to Government Health Coverage
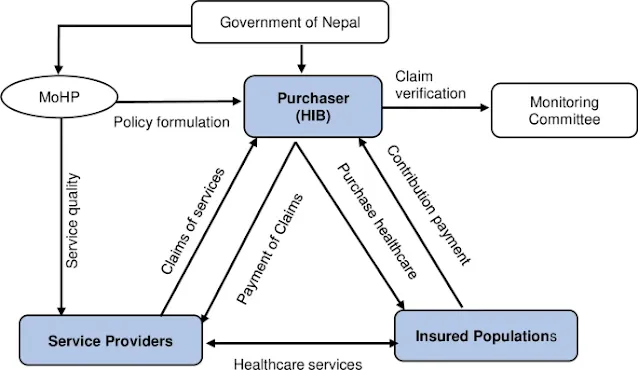
This is a program that aims to provide universal health coverage to all Nepali citizens by enrolling them in a community-based health insurance scheme. The National Health Insurance program was launched in 2016 by the Ministry of Health and Population, with the support of the World Bank and other development partners.The program operates at the ward level, which is the lowest administrative unit in Nepal. Each ward has a Ward Health Insurance Committee (WHIC), which is responsible for managing and implementing the program. The WHIC consists of representatives from the local government, health facilities, community groups, and beneficiaries. The WHIC registers the households in the ward, collects the premium, issues the health insurance cards, and monitors the service delivery and claim settlement.
The program covers a basic package of health services, which includes outpatient, inpatient, emergency, maternal and child health, family planning, immunization, and preventive and promotive services. The program also covers some chronic and expensive diseases, such as cancer, kidney failure, heart disease, and spinal cord injury. The program does not cover cosmetic, dental, and eye care services, except for cataract surgery.
The program is voluntary, but it encourages the participation of all households in the ward. The premium is based on the family size and income level, and ranges from Rs. 1,000 to Rs. 3,500 per year for a family of up to five members. The government subsidizes the premium for the poor, marginalized, and vulnerable groups, such as Dalits, Janajatis, senior citizens, single women, people with disabilities, and people living with HIV/AIDS. The government also provides a matching grant to the WHIC, based on the number of enrollees and the performance of the program.
The program is linked with the public and private health facilities in the district, which are contracted by the District Health Insurance Board (DHIB). The DHIB is responsible for accrediting, monitoring, and regulating the health facilities, and for reimbursing them for the services provided to the insured. The DHIB also coordinates with the Nepal Health Insurance Board (NHIB), which is the apex body for the program at the national level. The NHIB is responsible for setting the policy, standards, and guidelines for the program, and for providing technical and financial support to the DHIBs and WHICs.
The program has been implemented in 77 districts of Nepal, covering more than 7.4 million people as of November 2023. The program has shown positive results in terms of increasing the access, utilization, and quality of health services, and reducing the out-of-pocket expenditure and financial hardship of the people. The program has also contributed to the social inclusion and empowerment of the poor and marginalized groups, and to the strengthening of the health system and governance.
The program covers a basic package of health services, such as outpatient, inpatient, emergency, maternal and child health, family planning, immunization, and preventive and promotive services. The program also covers some chronic and expensive diseases, such as cancer, kidney failure, heart disease, and spinal cord injury. The program does not cover cosmetic, dental, and eye care services, except for cataract surgery.
The program is linked with the public and private health facilities in the district, which are contracted by the District Health Insurance Board. You can find the list of the health facilities on the website of Health Insurance Board or by asking your WHIC. You need to visit the nearest health facility in your area for any service, and you can get a referral to a higher level facility if needed.
You do not have to pay any fee or co-payment for the services, except for some nominal charges for medicines and consumables. You can also file a complaint or suggestion to your WHIC or the Health Insurance Board, if you are not satisfied with the service or the policy.
The program, however, faces some challenges, such as low awareness and enrollment, inadequate and irregular premium collection, insufficient and delayed claim settlement, limited and uneven service availability, and weak monitoring and evaluation. The program also needs to address the issues of sustainability, scalability, and integration with other social protection schemes.
The program is a commendable initiative that aims to achieve the vision of health for all in Nepal. It is a model of community-based and participatory health insurance that can be replicated and adapted in other countries. The program, however, requires continuous improvement and innovation to overcome the challenges and to meet the expectations and needs of the people.
How do I enroll in the Ward/ government health insurance program?
To enroll in the Ward/ government health insurance program in Nepal, you need to follow these steps:First, you need to contact your local Ward Health Insurance Committee (WHIC), which is responsible for managing and implementing the program in your area. You can find the contact details of your WHIC on the website of Health Insurance Board or by asking your local government or health facility.
Second, you need to register your household in the program by filling in an application form and providing the required documents, such as citizenship certificate, family details, income proof, etc. You can get the application form from your WHIC or download it from the website of Health Insurance Board.
Third, you need to pay the annual premium for your household, which is based on your family size and income level. The premium ranges from Rs. 1,000 to Rs. 3,500 per year for a family of up to five members, and Rs. 700 per additional member. You can pay the premium in cash or through online or mobile banking. You can also get a subsidy from the government if you belong to the poor, marginalized, or vulnerable groups, such as Dalits, Janajatis, senior citizens, single women, people with disabilities, and people living with HIV/AIDS.
Fourth, you need to collect your health insurance card from your WHIC, which will show your name, photo, address, and policy number. You need to show this card whenever you visit a health facility for any service covered by the program. You can also check your policy status and balance on the website of Health Insurance Board or by calling the toll-free number 1660-01-44444.
Fifth, you need to renew your policy every year by paying the premium and updating your information. You can also change your health facility or add or remove any family member from your policy, if needed. You need to inform your WHIC about any changes in your policy within 15 days.
By following these steps, you can enroll in the Ward/ government health insurance program in Nepal and enjoy the benefits of the program.
What are the documents required for enrolling in the program?
The documents required for enrolling in the Ward/ government health insurance program in Nepal are as follows:- Citizenship certificate of the head of the household or any other member who is applying for the program.
- Family details of the household, such as name, age, gender, relation, and occupation of each member.
- Income proof of the household, such as paystubs, tax returns, bank statements, or any other documents that show the source and amount of income of the household.
- Passport size photos of each member of the household who is applying for the program.
- Application form, which can be obtained from the Ward Health Insurance Committee (WHIC) or downloaded from the website of Health Insurance Board.
You need to submit these documents along with the premium payment to your WHIC, and collect your health insurance card.
Can I enroll in the program without any income proof?
You can enroll in the Ward/ government health insurance program in Nepal without any income proof, if you belong to the poor, marginalized, or vulnerable groups, such as Dalits, Janajatis, senior citizens, single women, people with disabilities, and people living with HIV/AIDS. These groups are eligible for a subsidy from the government, which covers the full or partial premium amount.However, you need to provide other documents, such as citizenship certificate, family details, and passport size photos, to register your household in the program. You also need to get a recommendation letter from your local government or ward office, which verifies your identity and economic status. If you do not belong to these groups, you need to provide income proof, such as paystubs, tax returns, bank statements, or any other documents that show the source and amount of income of your household.
The income proof is used to determine the premium amount, which ranges from Rs. 1,000 to Rs. 3,500 per year for a family of up to five members, and Rs. 700 per additional member.
What is the subsidy amount for the eligible groups?
The subsidy amount for the eligible groups in the Ward/ government health insurance program in Nepal varies depending on the economic status and the category of the groups.For the ultra-poor, marginalized, and vulnerable groups, such as Dalits, Janajatis, senior citizens, single women, people with disabilities, and people living with HIV/AIDS, the government bears the full premium amount, which is Rs. 3,500 per year for a family of up to five members, and Rs. 700 per additional member.
For the poor and low-income groups, such as farmers, laborers, and informal sector workers, the government bears 75% of the premium amount, which is Rs. 2,625 per year for a family of up to five members, and Rs. 525 per additional member.
For the middle-income groups, such as civil servants, teachers, and professionals, the government bears 50% of the premium amount, which is Rs. 1,750 per year for a family of up to five members, and Rs. 350 per additional member.
For the high-income groups, such as business owners, executives, and celebrities, the government bears 25% of the premium amount, which is Rs. 875 per year for a family of up to five members, and Rs. 175 per additional member.
The subsidy amount is determined by the local government or ward office, based on the recommendation letter and the poverty identity card or red card of the applicant. The subsidy amount is transferred to the Ward Health Insurance Committee (WHIC), which is responsible for managing and implementing the program in the area.
The subsidy amount is subject to change and may vary depending on the availability of funds and the performance of the program. You can find more information about the program and the subsidy amount on the website of Health Insurance Board or by contacting your WHIC.





Please leave your comments or ask your queries here. The comments shall be published only after the Admin approval.